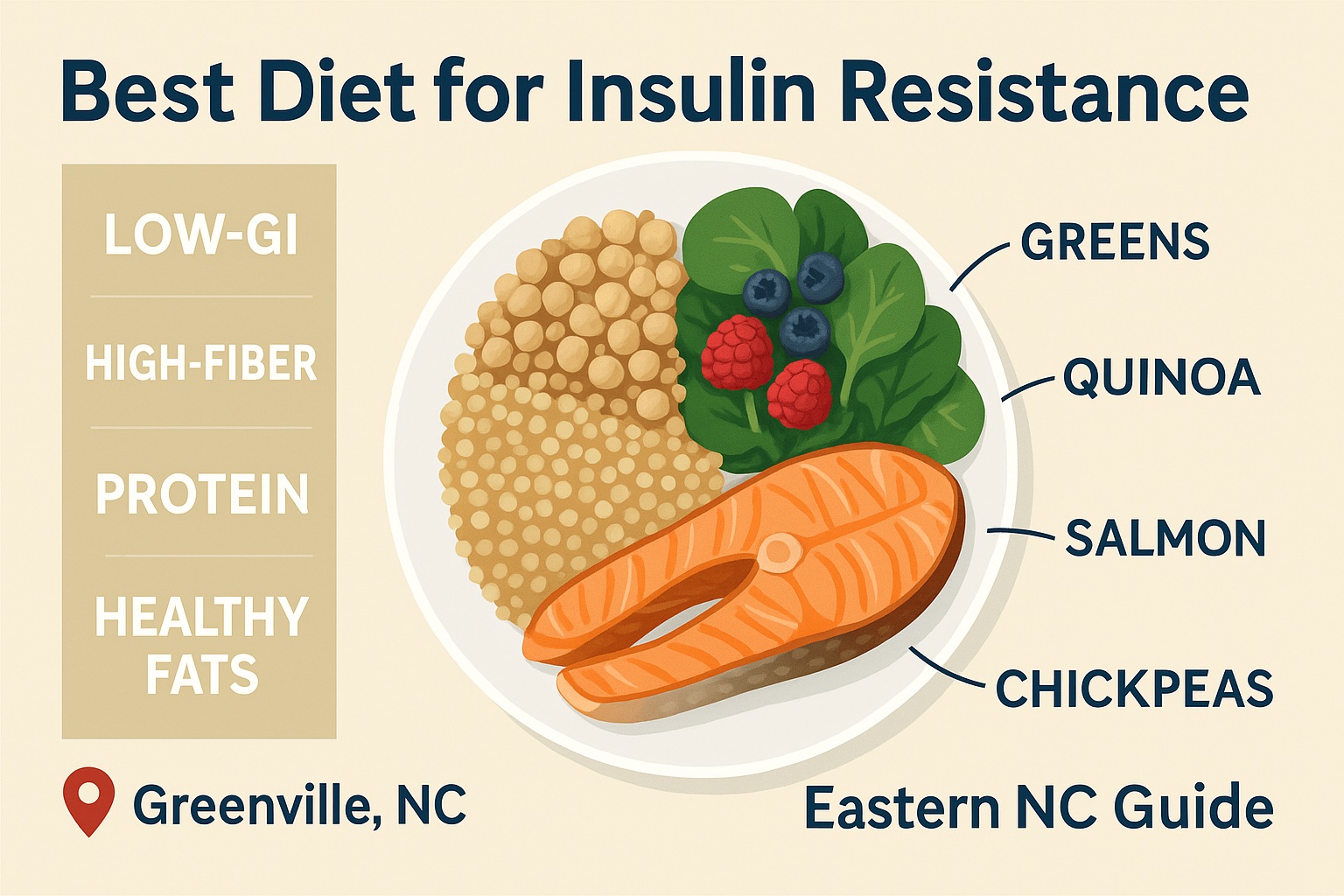
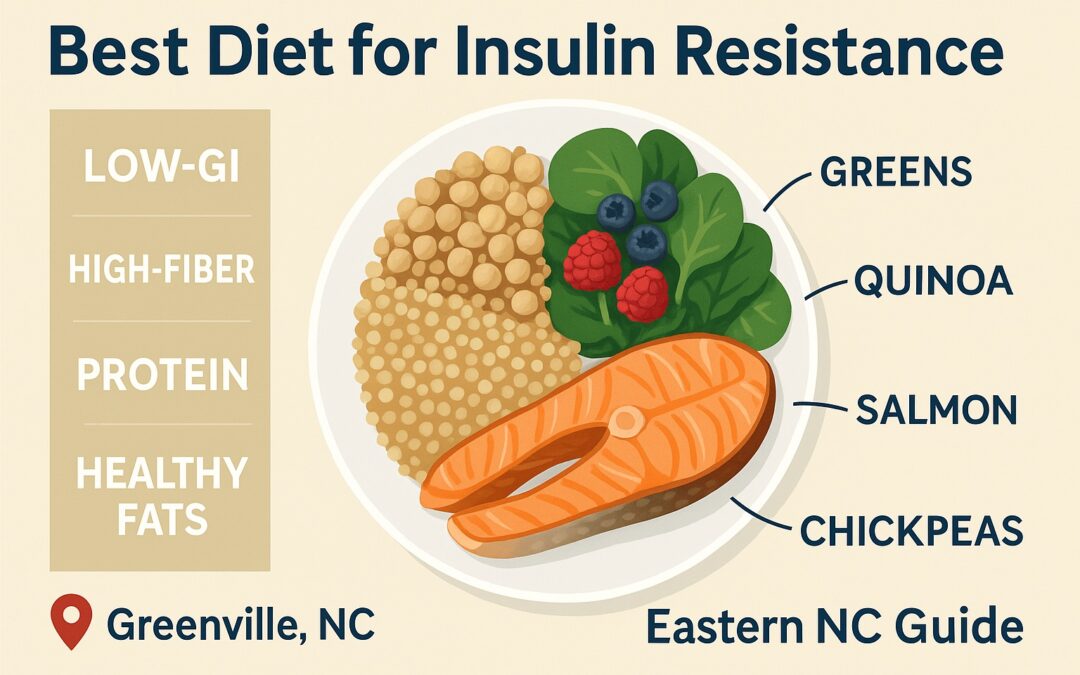
Best Diet for Insulin Resistance (Eastern NC Guide)
Short answer: The most consistent “best diet” for insulin resistance isn’t a single brand-name plan, it’s a pattern: low–glycemic index/high-fiber carbohydrates, adequate lean protein, and healthy fats (often a Mediterranean-style template), paired with regular activity. These approaches are first-line lifestyle strategies in current diabetes care guidance.
Quick Answer: What actually works?
- Carb quality over carb elimination: Choose low-GI, high-fiber carbs (beans, lentils, oats, quinoa, whole fruit), and limit refined starches/sugars.
- Mediterranean-style pattern: Vegetables, fruit, legumes, whole grains, fish, olive oil linked with improved insulin resistance markers.
- Protein at each meal: Helps satiety, supports lean mass during weight loss; many do well around ~1.2 g/kg/day (individualized).
- Healthy fats: Favor unsaturated fats (olive oil, nuts, seeds, avocado; fish) over saturated fats.
- Make activity non-negotiable: Aim for 150 minutes/week moderate activity + 2 strength days to enhance insulin sensitivity.
Eastern NC context: This guide includes Greenville-friendly meal ideas and local activity options so you can put the plan into practice right away.
Core Principles: Carb Quality, Fiber, Protein, Healthy Fats
Low-GI, High-Fiber Carbs
Insulin resistance improves when meals emphasize fibrous, minimally processed carbs and minimize refined starches/added sugars. A low-GI (or low-glycemic load) approach helps flatten post-meal spikes and improves insulin sensitivity in trials and reviews.
- Fill the plate with: Beans/lentils/chickpeas; steel-cut oats; quinoa; brown/wild rice blends; sweet potatoes; whole fruit (berries, apples, citrus).
- Limit: Sugary drinks/juices, pastries, white bread, fries, ultra-processed snacks.
- Pairing trick: When you eat carbs, add protein + healthy fat (e.g., apple + almonds; oats + Greek yogurt) to blunt glucose rise.
Protein Targets (and Why They Matter)
Ensuring adequate protein supports fullness and preserves lean mass during weight loss, both helpful for insulin sensitivity. In controlled settings, higher-protein diets (vs. standard) have improved insulin resistance and glycemic variability. Many people do well targeting roughly ~1.2 g/kg/day, distributed across meals; adjust with your clinician, especially if you have kidney disease or other conditions.
Healthy Fats & Meal Pairing
Favor unsaturated fats (olive oil, nuts, seeds, avocado; fish like salmon or mackerel). Swapping saturated fats for polyunsaturated fats is associated with better insulin sensitivity in randomized research.
Mediterranean-Style Template You Can Follow
Think of the Mediterranean diet as a flexible framework: plant-forward, fiber-rich, with lean proteins and olive-oil-based fats. Multiple studies link this pattern with improved insulin resistance and delayed progression to type 2 diabetes.
1-Day Sample Plate (Greenville-Friendly)
- Breakfast: Steel-cut oats cooked with milk/unsweetened soy, topped with berries, chia, and a spoon of Greek yogurt.
- Lunch: Lentil + quinoa bowl with mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, cucumber, olive oil + lemon; add grilled chicken or tofu.
- Dinner: Herb-baked salmon, roasted Brussels sprouts, small baked sweet potato with olive oil.
- Snacks: Apple + almonds; veggie sticks + hummus; cottage cheese + cinnamon.
Local tip: Use Eastern NC farmers markets for seasonal greens and sweet potatoes; pre-cook grains/legumes on Sunday for fast weekday bowls.
Movement That Makes Diet Work Better (150 min + Strength)
Diet changes work even better with regular activity. Aim for 150 minutes/week of moderate aerobic activity (e.g., brisk walking) plus 2 days/week of strength training. Short post-meal walks help with glucose control, and strength sessions increase muscle’s ability to use glucose. Explore Town Common paths, River Park North, or your neighborhood for 20–30-minute brisk walks.
FAQs
What diet is best for insulin resistance?
A pattern emphasizing low-GI/high-fiber carbs, lean protein, and healthy fats (frequently a Mediterranean-style approach) has consistent support. Individualize with your clinician based on labs, preferences, and any medications.
Do I need to cut all carbs?
No. Focus on carb quality and fiber, and pair carbs with protein/fat. Whole fruit is fine, watch portions and pair (e.g., fruit + nuts).
How much protein should I eat?
During weight loss, many adults do well around ~1.2 g/kg/day, spread across meals, to support fullness and lean mass. Check with your clinician for a personalized target.
How fast can I see changes?
Some people notice energy and post-meal glucose changes within weeks; lab markers (like fasting glucose) vary. Consistency matters more than perfection.
Next Step in Eastern NC
If you have prediabetes, elevated fasting glucose, or a family history, consider a consult. ECWL can review your labs, medications, and routine to tailor a plan and decide whether additional tools (e.g., medication) make sense for you.
Ask ECWL a Question | Learn about GLP-1 options & alternatives
Sources
- American Diabetes Association — Standards of Care in Diabetes 2025.
- CDC — Physical Activity Guidelines for Adults.
- Low-GI/GL dietary pattern evidence for insulin sensitivity.
- Mediterranean diet & insulin resistance outcomes.
- Higher-protein diets during weight loss & insulin resistance.
Disclaimer: This article is educational and not medical advice. Results vary. Consult your clinician, especially if you use glucose-lowering medication.